Navigating the Rhythms of Nature: Understanding the Forest Calendar
Related Articles: Navigating the Rhythms of Nature: Understanding the Forest Calendar
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Rhythms of Nature: Understanding the Forest Calendar. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Rhythms of Nature: Understanding the Forest Calendar

The forest, a complex and intricate ecosystem, operates on a cyclical rhythm dictated by the interplay of sunlight, temperature, and precipitation. This natural cadence, often referred to as the "forest calendar," provides a framework for understanding the dynamic processes that shape the life and growth of trees, plants, animals, and fungi within this vital environment.
Decoding the Forest Calendar: A Journey Through Time
The forest calendar is not a fixed, rigid schedule, but rather a nuanced tapestry woven from the interactions of various ecological factors. Each season brings its own unique set of conditions, influencing the behavior and development of forest inhabitants.
Spring: A Time of Renewal
As winter’s grip loosens, the forest awakens from its slumber. Rising temperatures and increasing sunlight trigger a surge of activity. Trees burst into leaf, their canopies transforming into vibrant green tapestries. Wildflowers carpet the forest floor, their blooms attracting pollinators. Animals emerge from hibernation, seeking food and mates.
-
Key Events:
- Budburst: Trees begin to sprout leaves, a critical stage for photosynthesis and energy production.
- Wildflower Bloom: A diverse array of wildflowers emerges, providing food and habitat for insects and other animals.
- Bird Migration: Many bird species return from their wintering grounds, seeking breeding territories and nesting sites.
- Animal Breeding: Various animal species engage in mating rituals, ensuring the continuation of their populations.
Summer: A Period of Growth and Abundance
Summer’s warmth and extended sunlight provide optimal conditions for growth and reproduction. Trees reach their peak foliage, providing shade and shelter. Fruits ripen, attracting a variety of animals. Insect populations flourish, contributing to pollination and food webs.
-
Key Events:
- Full Leaf Canopy: Trees reach maximum leaf production, maximizing photosynthesis and providing shade for the forest floor.
- Fruiting Season: A variety of trees and plants produce fruits, providing essential food sources for animals.
- Insect Activity: Insect populations peak, playing crucial roles in pollination, decomposition, and food webs.
- Animal Nesting: Many animals build nests and raise their young during this period of abundant resources.
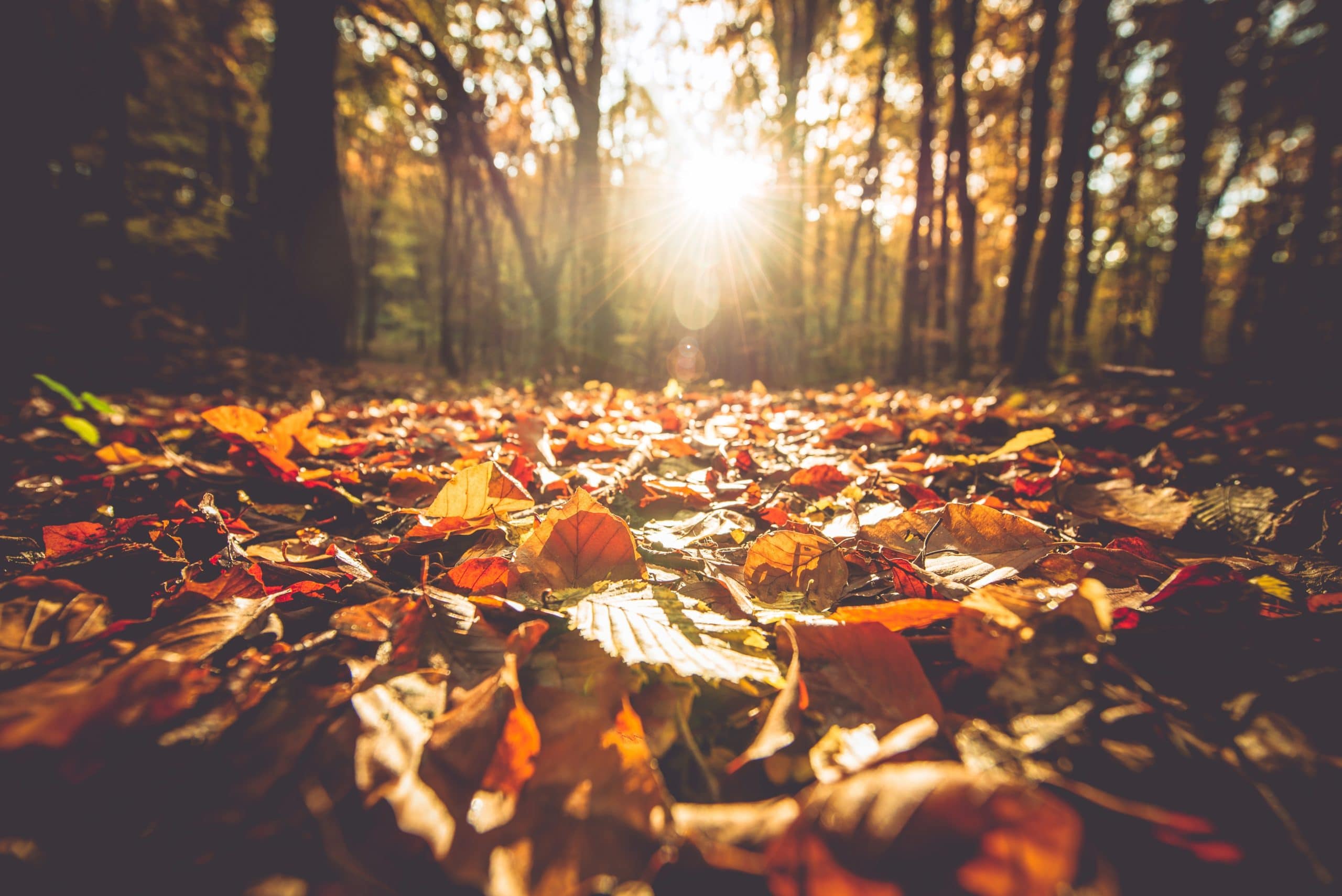
Autumn: A Time of Transition
As daylight hours shorten and temperatures cool, the forest prepares for winter. Leaves change color, displaying a spectacular kaleidoscope of hues before falling to the ground. Animals gather food and prepare for the colder months ahead.
-
Key Events:
- Fall Foliage: Leaves change color due to the breakdown of chlorophyll, revealing pigments like carotenoids and anthocyanins.
- Leaf Drop: Trees shed their leaves, conserving energy and preparing for dormancy.
- Animal Migration: Some animals migrate to warmer climates, seeking more favorable conditions for survival.
- Food Storage: Many animals gather and store food for the winter months, ensuring their survival during periods of scarcity.
Winter: A Time of Dormancy and Rest
Winter’s cold temperatures and reduced sunlight create a period of dormancy for many forest inhabitants. Trees stand bare, their growth halted. Animals hibernate or become less active, conserving energy. Decomposition processes slow down, contributing to the accumulation of organic matter on the forest floor.
-
Key Events:
- Tree Dormancy: Trees enter a state of reduced metabolic activity, conserving energy and surviving the harsh conditions.
- Animal Hibernation: Many animals enter a state of prolonged sleep, reducing their energy expenditure and surviving on stored fat reserves.
- Decomposition: Decomposition processes slow down, contributing to the accumulation of organic matter on the forest floor, which provides nutrients for future growth.
The Importance of Understanding the Forest Calendar
Understanding the forest calendar is essential for a variety of reasons:
- Forest Management: Foresters use the calendar to plan and implement sustainable harvesting practices, ensuring the long-term health and productivity of forests.
- Conservation Efforts: Conservationists rely on the calendar to understand the timing of sensitive periods for wildlife, such as breeding seasons, and to develop effective conservation strategies.
- Ecological Research: Scientists use the calendar to study the complex interactions between organisms and their environment, contributing to our understanding of ecological processes.
- Recreation and Tourism: Outdoor enthusiasts can use the calendar to plan activities that align with the seasonal changes in the forest, maximizing their enjoyment and minimizing their impact.
FAQs about the Forest Calendar
Q: How does the forest calendar vary across different regions?
A: The forest calendar is influenced by latitude, altitude, and local climate conditions. For example, forests in tropical regions experience less pronounced seasonal variation compared to those in temperate zones.
Q: Are there any specific events that mark the transition between seasons?
A: While the transition between seasons is gradual, certain events serve as indicators. For example, the arrival of migratory birds in spring, the first frost in autumn, or the first snowfall in winter can be considered markers of seasonal change.
Q: How does climate change affect the forest calendar?
A: Climate change is altering the timing and intensity of seasonal events, leading to shifts in the forest calendar. Warmer temperatures, altered precipitation patterns, and more frequent extreme weather events can disrupt the natural rhythms of the forest, impacting the timing of budburst, leaf drop, and other key events.
Tips for Observing the Forest Calendar
- Keep a Field Journal: Record your observations of seasonal changes in the forest, noting the timing of leaf emergence, flowering, fruiting, and animal behavior.
- Visit the Forest Regularly: Make repeated visits to the forest throughout the year, allowing you to track the progression of seasonal changes.
- Pay Attention to the Small Details: Observe the subtle changes in the forest, such as the emergence of new plant growth, the arrival of migratory birds, or the sounds of insects buzzing.
- Learn about the Local Flora and Fauna: Familiarize yourself with the trees, plants, animals, and insects that inhabit your local forest.
Conclusion
The forest calendar is a powerful tool for understanding the intricate web of life within this vital ecosystem. By recognizing the rhythms of nature, we can appreciate the dynamic processes that shape the forest and develop more sustainable and responsible practices for managing and conserving this precious resource. Through observation and understanding, we can become better stewards of the forest, ensuring its health and vitality for generations to come.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Rhythms of Nature: Understanding the Forest Calendar. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!